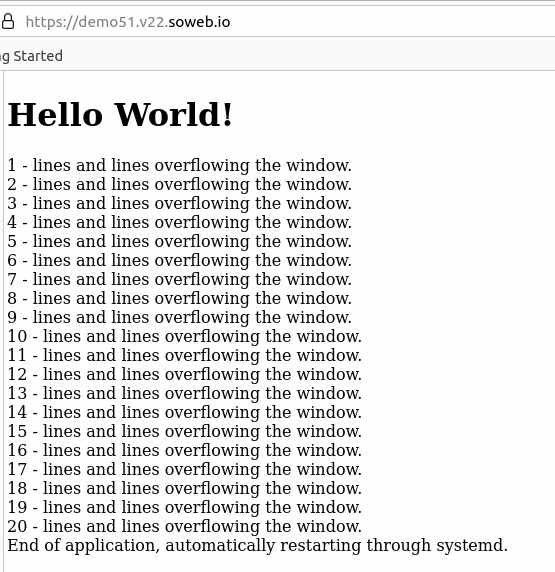
Description
Hello World! is the simplest Gnoga App ever. It is a single user application and will be restarted automatically after each run.
This tutorial is designed to introduce the most basic concepts of Gnoga:
- Gnoga.Application.* – Initialize connectivity and application termination.
- Gnoga.Gui.Window – The connection to the browser window.
- Gnoga.Gui.View.* – Gui element containers attached to the window.
Source code
with Gnoga.Application.Singleton;
-- Gnoga offers various types of application packages. These packages manage
-- the connectivity with the browser and your application.
--
-- The Singleton package is designed to allow for simple one time run
-- applications much like your typical desktop applications that run
-- sequentially from start to completion by one single user.
with Gnoga.Gui.Window;
-- All Gnoga GUI related packages are in Gnoga.Gui.*
-- Gnoga.Gui.Window.Window_Type abstracts the Browser window.
with Gnoga.Gui.View.Console;
-- There are many ways to write Gnoga programs, attaching a View to a
-- a Window is one of the easiest ways. Different view types provide
-- different ways to organize or place GUI elements.
-- Gnoga.Gui.View.Console.Console_Type automatically adds new GUI elements
-- to the next row in the view and provides scroll bars for the over flow.
-- It also provides a simple console like way to add HTML or text to the
-- page using its Put_Line method.
procedure Tutorial_01 is
use Gnoga;
use all type Gnoga.String;
My_Window : Gnoga.Gui.Window.Window_Type;
-- My_Window will be connected during Initialize to the browser.
My_View : Gnoga.Gui.View.Console.Console_View_Type;
-- My_View when created will attach itself to My_Window and manage our GUI
-- view in the browser.
begin
Gnoga.Application.Title ("Tutorial 01");
-- Before starting our application, we can set its title.
-- This title will appear on the browser title when the browser
-- connects to our application.
-- Gnoga.Application.Open_URL_* could be used here to start the user's
-- default browser pointing to this tutorial application.
Gnoga.Application.Singleton.Initialize (Main_Window => My_Window);
-- Initialize will start Gnoga's http services and websocket services
-- to wait for a connection from the browser. There are ways to start
-- a browser and have it connected on startup or use customized browser
-- applications to give your application a native executable like any other
-- desktop application. This will be explored in future tutorials.
--
-- Initialize blocks until the browser connects. My_Window is now a
-- live connection to the browser.
-- For example we can tell the browser to pop an alert box:
My_Window.Alert ("Hello World!");
-- Now that we got the alert box out of the way, lets create our View
My_View.Create (My_Window);
-- The Console_View_Type has the handy ability to shut down the application
-- when the browser window is closed.
-- Now we can now start talking to our view
My_View.Put_HTML ("<H1>Hello World!</H1>");
for i in 1 .. 50 loop
My_View.Put_Line (Image (i) & " - lines and lines overflowing the window.");
end loop;
Gnoga.Application.Singleton.End_Application;
-- Terminate our connection to the browser and end the application
end Tutorial_01;Project file
with "settings.gpr";
with "gnoga.gpr";
project Tutorial_01 is
for Object_Dir use Settings.Obj_Dir;
for Exec_Dir use Settings.Exe_Dir;
for Main use ("tutorial_01.adb");
for Create_Missing_Dirs use Settings'Create_Missing_Dirs;
package Compiler renames Settings.Compiler;
package Binder renames Settings.Binder;
package Linker renames Settings.Linker;
package Pretty_Printer renames Settings.Pretty_Printer;
end Tutorial_01;